
Right side of our picture has “-“sign in front of the Vy because its direction is downward. At the same levels magnitudes of Vy are the same however, their signs are opposite.
PROJECTILE PHYSICS CALCULATOR FREE
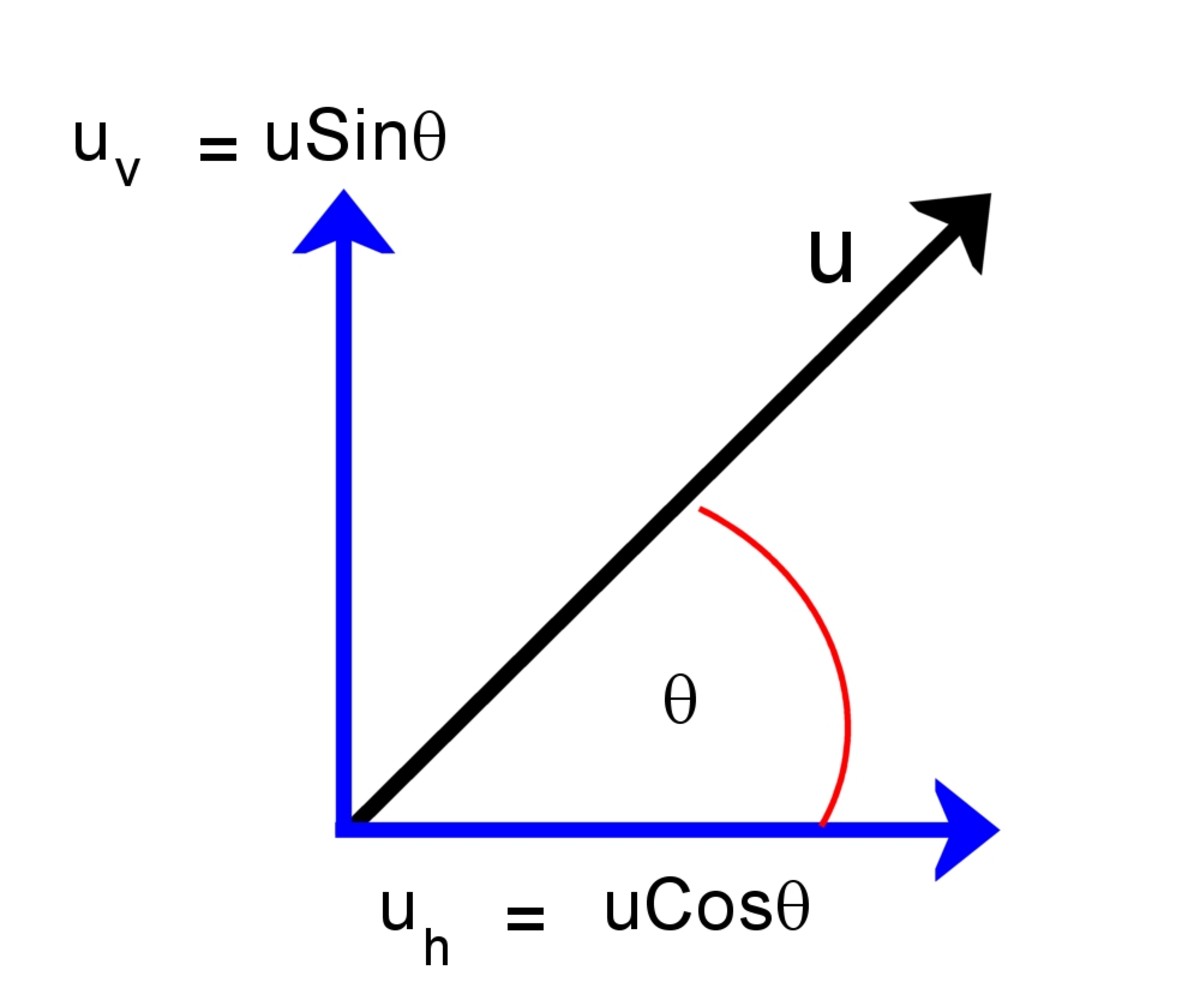
After Vy becomes zero our ball changes its direction and make free fall now. At the top where it reaches its maximum height vertical component of our velocity becomes zero as in the case of free fall examples. In vertical as you can see in the picture, our velocity is decreasing in the amount of gravitational acceleration. When we look at the horizontal motion of the object we see that it looks like example solved in free fall motion section. We examine our motion in two parts, first one is horizontal motion and second one is vertical motion. If we look at the forces acting on our ball we see only the gravity as a force. Vx and Vy are the X and Y components of our velocity. V is its velocity and its direction is northeast. At the beginning the ball is thrown with an angle to the horizontal. First, look at the given picture which shows the motion path, velocities in different points and forces acting upon the object doing projectile motion.Īs you see in the picture given above, we have a projectile motion and velocity components at different positions. I will explain this sentence with a picture and examples. In projectile motion, gravity is the only force acting on the object. For example, you throw the ball straight upward, or you kick a ball and give it a speed at an angle to the horizontal or you just drop things and make them free fall all these are examples of projectile motion. We can have different types of projectile type. In this type of motion gravity is the only factor acting on our objects. Now, we will try to explain motion in two dimensions that is exactly called “projectile motion”. Hmax = h - initial height from which we're launching the object is the maximum height in projectile motion.We see one dimensional motion in previous topics. As sine of 0° is 0, then the second part of the equation disappears, and we obtain : If α = 0°, then vertical velocity is equal to 0 (Vy = 0), and that's the case of horizontal projectile motion. Hmax = h + V₀² / (4 * g) and in that case, the range is maximal if launching from the ground (h = 0). If α = 45°, then the equation may be written as: Also, you may want to have a look at our even more accurate equivalent - the free fall with air resistance calculator. If, additionally, Vy = 0, then it's the case of free fall. Hmax = h + V₀² / (2 * g) and the time of flight is the longest. If α = 90°, then the formula simplifies to: Let's discuss some special cases with changing angle of launch: Hmax = V₀² * sin(α)² / g – g * (V₀ * sin(α) / g)² / 2Īnd what if we launch a projectile from some initial height h? No worries! Apparently, the calculations are a piece of cake - all you need to do is add this initial elevation! So, given y = hmax and t = th, we can join those two equations together:
The formula describing vertical distance is: It means that at the highest point of projectile motion, the vertical velocity is equal to 0 (Vy = 0).įrom that equation we can find the time th needed to reach the maximum height hmax: The object is flying upwards before reaching the highest point - and it's falling after that point. Maximum height of the object is the highest vertical position along its trajectory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
